Why is dehydration dangerous?
Dehydration, a condition where the body does not have enough water to function correctly, poses significant health risks. Water plays a vital role in various bodily functions; therefore, a deficiency can lead to a myriad of complications, ranging from mild to severe. This article will delve into the importance of hydration, the dangers posed by dehydration, its signs and symptoms, and ways to prevent it.
1. Understanding the Role of Water in the Body:
Before we can fully comprehend the dangers of dehydration, it's essential to understand water's crucial role in our bodies. Our bodies are approximately 60% water, making it a primary component of our makeup. Water facilitates a multitude of functions, including:
Regulation of body temperature: Through processes like sweating and respiration, water helps keep our temperature steady.
Lubrication of joints: Water keeps our joints lubricated, reducing friction and wear.
Digestion: Saliva, primarily made of water, aids in the breakdown of food, and water also aids in nutrient absorption in the gut.
Detoxification: Our kidneys and liver rely on adequate water to filter waste products and toxins.
Cellular function: Cells need water to function and maintain their shape and structure.
2. Consequences of Dehydration:
When the body doesn't receive adequate water, several complications can arise:
Impaired Cognitive Function: Dehydration can lead to difficulty concentrating, reduced alertness, and short-term memory issues.
Kidney Damage: The kidneys need water to filter waste from the blood. Chronic dehydration can lead to kidney stones and, in severe cases, kidney failure.
Heat-related Illnesses: These range from mild heat cramps to potentially fatal heatstroke.
Urinary Tract Infections: Reduced urine output due to dehydration can lead to UTIs or bladder infections.
Hypovolemic Shock: A severe form of dehydration where low blood volume causes a drop in blood pressure and the amount of oxygen in the body. This can be life-threatening.
Seizures: Electrolytes—like potassium and sodium—help transmit electrical signals. When these are out of balance due to dehydration, it can lead to seizures.
Digestive Issues: Dehydration can cause a dry mouth, leading to bad breath and decreased saliva production, which affects digestion. It can also cause constipation.
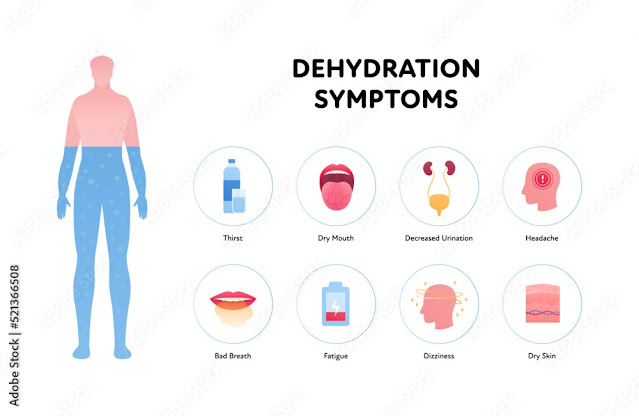
3. Recognizing the Signs of Dehydration:
Understanding the signs of dehydration allows for timely intervention. These signs include:
- Dark yellow urine or reduced urine output.
- Dry mouth and dry skin.
- Rapid heartbeat and rapid breathing.
- Fatigue or dizziness.
- Confusion or irritability.
- Extreme thirst.
- Headache or light-headedness.
4. Preventing Dehydration:
Prevention is the best way to counteract the dangers posed by dehydration. Here are some steps to ensure you stay hydrated:
Monitor Fluid Intake: Aim for at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water daily, more if you're active or in hot climates.
Eat Water-rich Foods: Foods like cucumbers, oranges, strawberries, and melons can supplement fluid intake.
Limit Diuretics: Beverages like coffee, tea, and certain sodas can increase urine production, potentially leading to dehydration if consumed in large amounts.
Rehydrate After Exercise: Drink more fluids to compensate for what's lost through sweat.
Carry a Water Bottle: Having water on hand can remind you to drink periodically.
Conclusion:
Water is, without a doubt, essential for our survival and overall well-being. Dehydration, if left unchecked, can lead to severe health complications that can be potentially life-threatening. Being aware of the importance of adequate hydration and understanding how to prevent dehydration is crucial for maintaining optimal health. The next time you reach for a glass of water, remember the essential role it plays in keeping your body functioning at its best.
1. How does dehydration affect bodily functions?
2. Why is maintaining fluid balance crucial for the brain?
3. What complications can arise from prolonged dehydration?
4. How does dehydration impact the cardiovascular system?
5. What role does hydration play in regulating body temperature?




.png)



0 Comments
please do not enter spam link in the comment box.